Recent research has proven that compounds found in the cannabis plant can have a positive effect on gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) levels in the brain.
GABA is thought to have a natural calming effect and is believed to reduce feelings of anxiety and fear by decreasing neuronal excitability, thus giving way to new research suggesting medical marijuana as a treatment for anxiety disorders.
In addition to cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), medication is frequently prescribed for patients suffering from anxiety disorders. One of the most common are benzodiazepines, a class of agents that work on gamma-aminobutyric acid-A (GABA-A) receptors in the brain.
Unfortunately, “benzos” have increasingly been associated with drug overdose due to their addictive properties, giving way to a demand for medically-proven, less destructive treatments such as medical marijuana for anxiety.
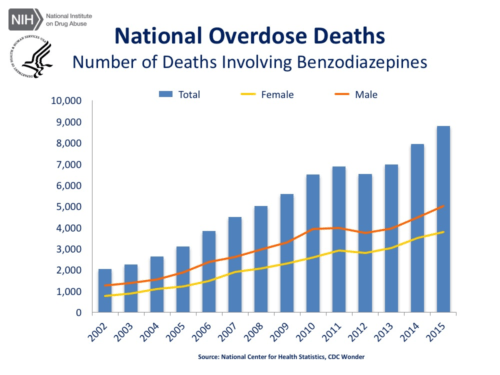
Source: DrugAbuse.gov
MEDICAL EVIDENCE IN SUPPORT OF USING MEDICAL MARIJUANA TO TREAT ANXIETY
Research has suggested that some of the main phytocannabinoids — specifically, the phytocannabinoid cannabigerol (CBG) — have been shown to have positive effects on receptors in the brain that cause anxiety.
Furthermore, the majority of users in studies report that consumption results in “euphoria, relaxation, heightened perception, sociability and creativity.”
An additional study performed to research CBD as an anxiolytic (anti-anxiety drug), showcased results where CBD was shown to reduce anxiety in patients with social anxiety disorder.
In short, multiple studies have provided evidence that medical marijuana is an effective anxiety treatment.
MEDICAL EVIDENCE AGAINST USING MEDICAL MARIJUANA TO TREAT ANXIETY
In a research publication called Cannabis and Anxiety: A Critical Review of the Evidence, researchers set out to review the nature of cannabis use and anxiety, as well as the clinical viability.
While it was found that cannabis users have a high prevalence of anxiety disorders and patients with anxiety disorders have high rates of cannabis use, there was no clear evidence that cannabis usage increases long-lasting anxiety disorders. Furthermore, these studies set out to look at the use of cannabis rather than pharmacological options such as phytocannabinoids, meaning that the research cited marijuana smokers and not users of pharmaceuticals.
It should be noted that the response to THC varies depending on a number of factors such as genetics and other environmental factors, as well as the concentrations of THC and other alkaloids in the plant itself.
ANXIETY OVERVIEW
Anxiety is defined as an excessive emotional responsiveness to an imminent event or something with an uncertain outcome. Anxiety disorders affect some 40 million people in the U.S. alone, making it the most common group of mental illnesses in the United States.
According to classifications of anxiety disorders, the main diagnostic entities are:
- generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), featuring general irritability, anxiety attacks, chronic apprehension/anxious expectation and secondary phobic avoidance.
- panic disorder, characterized by brief (2-10 min) spells of overwhelming anxiety or fear, accompanied by somatic and cognitive symptoms;
- social anxiety disorder (or social phobia), defined as extreme agitation in social contexts and avoidance of social situations;
- obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), characterized by recurrent and intrusive anxiogenic thoughts (obsessions), and stereotyped behaviors (compulsions) aimed at the reduction of the distress caused by the obsessions.
- post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), in which a prior intense trauma results in a long-lasting anxious response, with re-experiencing/flashback phenomena, avoidance and emotional numbing.
The pharmacological strategies for the treatment of anxiety disorders greatly depend on the diagnosis:
- Generalized anxiety disorder
- Benzodiazepines
- Buspirone
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
- Panic attack
- High-potency benzodiazepines
- Tricyclic antidepressants
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors
- Post-traumatic stress disorder
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
- Low-dose antipsychotic agents
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder
- Tricyclic antidepressants
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
TRYING MEDICAL MARIJUANA TREATMENT FOR ANXIETY DISORDERS
Patients with anxiety disorder have shown positive results with the usage of medical marijuana. If you are interested in trying medical marijuana for your anxiety or are inquiring for a loved one, you should first seek out your state laws to determine the legality of the drug in your state, the types of medicine you can use, where to get it, and how much you need.
If you are located in Florida, check out THC Physicians for your medical evaluation, the first step in getting a Florida Medical Marijuana Card.
